
You risk losing principal if you need money from a bond before it matures and you have to sell it when the price is low. When interest rates rise, bond prices fall.
Interest rate risk - When interest rates fall, bond prices rise. Interest, credit, inflation and call risk: The yield reflects the approximate measure of returns to the investor. The coupon is the annual interest rate the issuer promises to pay the holder each year, usually expressed as a percentage of par value (the amount the issuer originally borrowed and is obligated to pay back when the bond matures) of the security. What is the difference between coupon and yield for fixed income securities? Instead of buying bonds that are scheduled to come due during the same year, you purchase bonds that mature at staggered future dates. You can find details for frequency and date of payment by clicking the description of the bond.īond laddering is a strategy that can help minimize exposure to interest rate fluctuations. Payments are generally made in semiannual installments, based on the dates set in the initial POS (Preliminary Offering Statement). Annual interest payments are calculated by multiplying the bond's face value by the coupon rate. 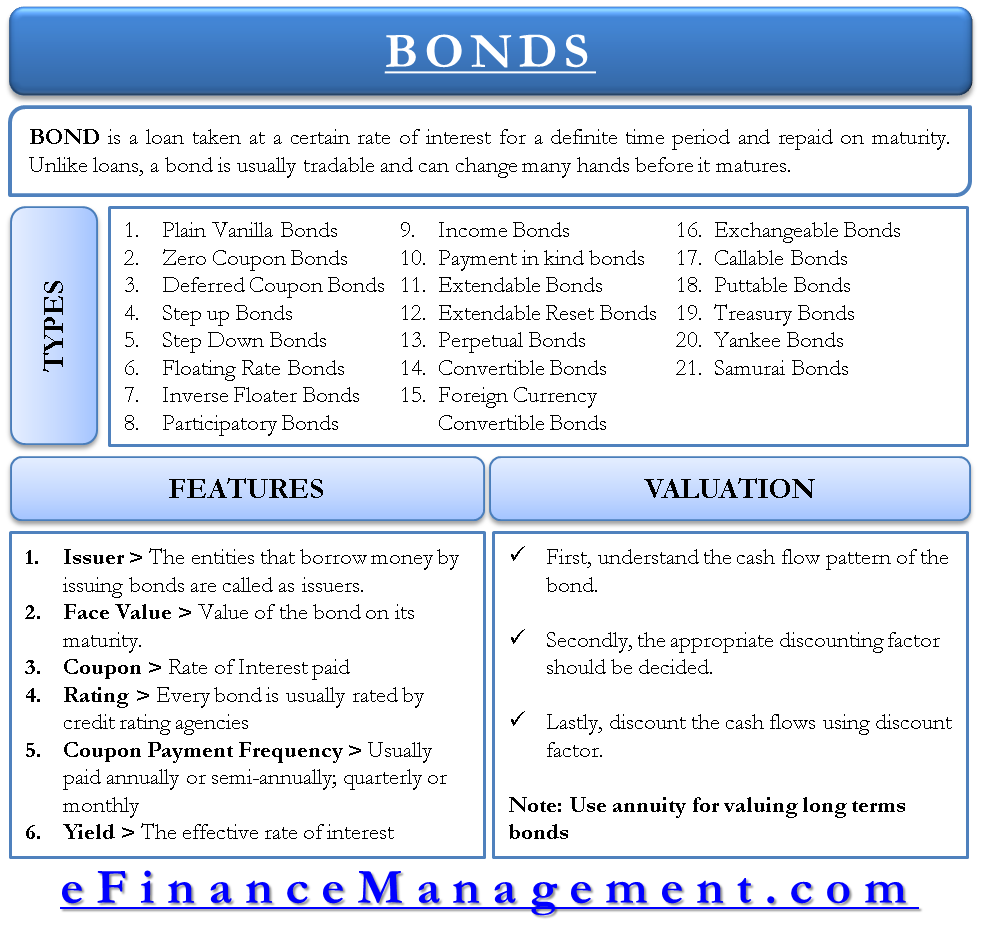
When a bond's price moves up or down, it still pays the same interest to the holder. What happens to my interest payment if rates go up or down? The amount a bond pays is largely determined by the prevailing interest rate and factors specific to that bond. Interest payments generally account for the bulk of a bond's return and are based on the bond's coupon (interest received on a bond) which is usually fixed for the life of the bond (although, some bonds have variable rates). When you buy a bond, the quoted yield considers the bond's annual interest rate and any difference between the purchase price and the amount you're expected to receive upon maturity or issuer call (the par or face value). There are a variety of ways to invest in fixed income (e.g., individual bonds and CDs, bond mutual funds and ETFs, or managed accounts).
Select ways to invest: Once you've defined your allocation, consider the ways in which you might invest. Choose an allocation: By combining bond investments with varying maturities and credit ratings, you can create fixed income portfolios that align with various levels of risk and are designed to meet different financial goals. Define a goal: Start by clarifying your reasons for adding fixed income to your portfolio: Is it to help preserve capital, diversify your portfolio, or generate income?. 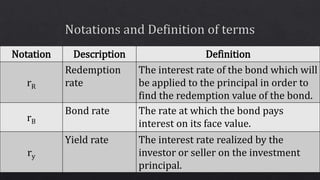
Whether you plan to build your own fixed income portfolio or have it professionally constructed, understanding the steps involved can help you feel more informed moving forward.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
